Compare commits
3 Commits
0e1f96d20b
...
e793d395bd
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| e793d395bd | |||
| 11967da94a | |||
| 930aa7cee8 |
38
0076_minimum-window-substring/README.md
Normal file
38
0076_minimum-window-substring/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
Given two strings `s` and `t` of lengths `m` and `n` respectively, return _the **minimum window substring** of_ `s` _such that every character in_ `t` _(**including duplicates**) is included in the window. If there is no such substring__, return the empty string_ `""`_._
|
||||
|
||||
The testcases will be generated such that the answer is **unique**.
|
||||
|
||||
A **substring** is a contiguous sequence of characters within the string.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 1:**
|
||||
|
||||
Input: s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"
|
||||
Output: "BANC"
|
||||
Explanation: The minimum window substring "BANC" includes 'A', 'B', and 'C' from string t.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 2:**
|
||||
|
||||
Input: s = "a", t = "a"
|
||||
Output: "a"
|
||||
Explanation: The entire string s is the minimum window.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 3:**
|
||||
|
||||
Input: s = "a", t = "aa"
|
||||
Output: ""
|
||||
Explanation: Both 'a's from t must be included in the window.
|
||||
Since the largest window of s only has one 'a', return empty string.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Constraints:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `m == s.length`
|
||||
* `n == t.length`
|
||||
* `1 <= m, n <= 105`
|
||||
* `s` and `t` consist of uppercase and lowercase English letters.
|
||||
|
||||
**Follow up:** Could you find an algorithm that runs in `O(m + n)` time?
|
||||
|
||||
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring
|
||||
42
0076_minimum-window-substring/python3/brute_force_tle.py
Normal file
42
0076_minimum-window-substring/python3/brute_force_tle.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
from collections import Counter
|
||||
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:
|
||||
tcounts = Counter(t)
|
||||
|
||||
# If chars of t is not included in the entire
|
||||
# s string, then we can just return right away
|
||||
if not tcounts <= Counter(s):
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
|
||||
tlen = len(t)
|
||||
min_window = ""
|
||||
|
||||
for start in range(len(s)):
|
||||
end = start + tlen - 1
|
||||
|
||||
# We can all the substrings starting from `start` which is every
|
||||
# letter of s
|
||||
while end < len(s):
|
||||
curr_window = s[start:end + 1]
|
||||
curr_window_counts = Counter(curr_window)
|
||||
|
||||
# <= is overloaded for Counters to mean inclusion
|
||||
#
|
||||
# i.e, counter_a -is-included-in- counter_b
|
||||
#
|
||||
if tcounts <= curr_window_counts:
|
||||
# If no min_window has been computed yet or if current
|
||||
# window is shorter, then we assign that as the new
|
||||
# min_window
|
||||
if min_window == "" or len(curr_window) < len(min_window):
|
||||
min_window = curr_window
|
||||
|
||||
# Since at this point, if we keep iterating in the inner loop,
|
||||
# we'll only get longer substrings so we just break and proceed
|
||||
# to find the substrings starting from the next letter (start + 1)
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
end += 1
|
||||
|
||||
return min_window
|
||||
0
0076_minimum-window-substring/python3/solution.py
Normal file
0
0076_minimum-window-substring/python3/solution.py
Normal file
30
0226_invert-binary-tree/README.md
Normal file
30
0226_invert-binary-tree/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
Given the `root` of a binary tree, invert the tree, and return _its root_.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 1:**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
|
||||
Output: [4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 2:**
|
||||
|
||||
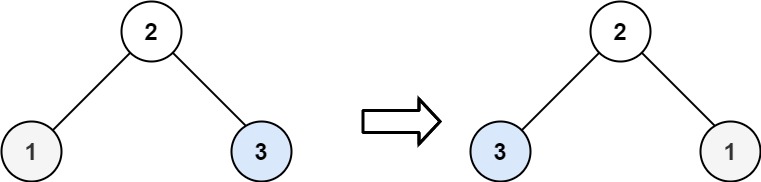
|
||||
|
||||
Input: root = [2,1,3]
|
||||
Output: [2,3,1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 3:**
|
||||
|
||||
Input: root = []
|
||||
Output: []
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Constraints:**
|
||||
|
||||
* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[0, 100]`.
|
||||
* `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
|
||||
|
||||
https://leetcode.com/problems/invert-binary-tree
|
||||
16
0226_invert-binary-tree/python3/solution.py
Normal file
16
0226_invert-binary-tree/python3/solution.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
# class TreeNode:
|
||||
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||||
# self.val = val
|
||||
# self.left = left
|
||||
# self.right = right
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def invertTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
|
||||
if root is None: return None
|
||||
|
||||
root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left
|
||||
|
||||
self.invertTree(root.left)
|
||||
self.invertTree(root.right)
|
||||
|
||||
return root
|
||||
73
1512_design-underground-system/README.md
Normal file
73
1512_design-underground-system/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
An underground railway system is keeping track of customer travel times between different stations. They are using this data to calculate the average time it takes to travel from one station to another.
|
||||
|
||||
Implement the `UndergroundSystem` class:
|
||||
|
||||
* `void checkIn(int id, string stationName, int t)`
|
||||
* A customer with a card ID equal to `id`, checks in at the station `stationName` at time `t`.
|
||||
* A customer can only be checked into one place at a time.
|
||||
* `void checkOut(int id, string stationName, int t)`
|
||||
* A customer with a card ID equal to `id`, checks out from the station `stationName` at time `t`.
|
||||
* `double getAverageTime(string startStation, string endStation)`
|
||||
* Returns the average time it takes to travel from `startStation` to `endStation`.
|
||||
* The average time is computed from all the previous traveling times from `startStation` to `endStation` that happened **directly**, meaning a check in at `startStation` followed by a check out from `endStation`.
|
||||
* The time it takes to travel from `startStation` to `endStation` **may be different** from the time it takes to travel from `endStation` to `startStation`.
|
||||
* There will be at least one customer that has traveled from `startStation` to `endStation` before `getAverageTime` is called.
|
||||
|
||||
You may assume all calls to the `checkIn` and `checkOut` methods are consistent. If a customer checks in at time `t1` then checks out at time `t2`, then `t1 < t2`. All events happen in chronological order.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 1:**
|
||||
|
||||
Input
|
||||
["UndergroundSystem","checkIn","checkIn","checkIn","checkOut","checkOut","checkOut","getAverageTime","getAverageTime","checkIn","getAverageTime","checkOut","getAverageTime"]
|
||||
[[],[45,"Leyton",3],[32,"Paradise",8],[27,"Leyton",10],[45,"Waterloo",15],[27,"Waterloo",20],[32,"Cambridge",22],["Paradise","Cambridge"],["Leyton","Waterloo"],[10,"Leyton",24],["Leyton","Waterloo"],[10,"Waterloo",38],["Leyton","Waterloo"]]
|
||||
|
||||
Output
|
||||
[null,null,null,null,null,null,null,14.00000,11.00000,null,11.00000,null,12.00000]
|
||||
|
||||
Explanation
|
||||
UndergroundSystem undergroundSystem = new UndergroundSystem();
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkIn(45, "Leyton", 3);
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkIn(32, "Paradise", 8);
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkIn(27, "Leyton", 10);
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkOut(45, "Waterloo", 15); // Customer 45 "Leyton" -> "Waterloo" in 15-3 = 12
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkOut(27, "Waterloo", 20); // Customer 27 "Leyton" -> "Waterloo" in 20-10 = 10
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkOut(32, "Cambridge", 22); // Customer 32 "Paradise" -> "Cambridge" in 22-8 = 14
|
||||
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Paradise", "Cambridge"); // return 14.00000. One trip "Paradise" -> "Cambridge", (14) / 1 = 14
|
||||
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Leyton", "Waterloo"); // return 11.00000. Two trips "Leyton" -> "Waterloo", (10 + 12) / 2 = 11
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkIn(10, "Leyton", 24);
|
||||
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Leyton", "Waterloo"); // return 11.00000
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkOut(10, "Waterloo", 38); // Customer 10 "Leyton" -> "Waterloo" in 38-24 = 14
|
||||
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Leyton", "Waterloo"); // return 12.00000. Three trips "Leyton" -> "Waterloo", (10 + 12 + 14) / 3 = 12
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 2:**
|
||||
|
||||
Input
|
||||
["UndergroundSystem","checkIn","checkOut","getAverageTime","checkIn","checkOut","getAverageTime","checkIn","checkOut","getAverageTime"]
|
||||
[[],[10,"Leyton",3],[10,"Paradise",8],["Leyton","Paradise"],[5,"Leyton",10],[5,"Paradise",16],["Leyton","Paradise"],[2,"Leyton",21],[2,"Paradise",30],["Leyton","Paradise"]]
|
||||
|
||||
Output
|
||||
[null,null,null,5.00000,null,null,5.50000,null,null,6.66667]
|
||||
|
||||
Explanation
|
||||
UndergroundSystem undergroundSystem = new UndergroundSystem();
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkIn(10, "Leyton", 3);
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkOut(10, "Paradise", 8); // Customer 10 "Leyton" -> "Paradise" in 8-3 = 5
|
||||
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Leyton", "Paradise"); // return 5.00000, (5) / 1 = 5
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkIn(5, "Leyton", 10);
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkOut(5, "Paradise", 16); // Customer 5 "Leyton" -> "Paradise" in 16-10 = 6
|
||||
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Leyton", "Paradise"); // return 5.50000, (5 + 6) / 2 = 5.5
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkIn(2, "Leyton", 21);
|
||||
undergroundSystem.checkOut(2, "Paradise", 30); // Customer 2 "Leyton" -> "Paradise" in 30-21 = 9
|
||||
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Leyton", "Paradise"); // return 6.66667, (5 + 6 + 9) / 3 = 6.66667
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Constraints:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `1 <= id, t <= 106`
|
||||
* `1 <= stationName.length, startStation.length, endStation.length <= 10`
|
||||
* All strings consist of uppercase and lowercase English letters and digits.
|
||||
* There will be at most `2 * 104` calls **in total** to `checkIn`, `checkOut`, and `getAverageTime`.
|
||||
* Answers within `10-5` of the actual value will be accepted.
|
||||
|
||||
https://leetcode.com/problems/design-underground-system
|
||||
40
1512_design-underground-system/python3/solution.py
Normal file
40
1512_design-underground-system/python3/solution.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
# Time: O(N)
|
||||
# Space: O(P) P is num of passengers who checkin at same time worst case
|
||||
# + O(S^2) S is num of stations, pair up every station so S^2 permutation
|
||||
|
||||
class UndergroundSystem:
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self.checkins = {}
|
||||
self.totals = {}
|
||||
|
||||
def checkIn(self, id: int, stationName: str, t: int) -> None:
|
||||
self.checkins[id] = (stationName, t)
|
||||
|
||||
def checkOut(self, id: int, endStation: str, end_t: int) -> None:
|
||||
startStation, start_t = self.checkins[id]
|
||||
|
||||
key = (startStation, endStation)
|
||||
duration = end_t - start_t
|
||||
|
||||
curr_total = self.totals.get(key, (0, 0))
|
||||
|
||||
# Increment total and count of journeys
|
||||
self.totals[key] = (curr_total[0] + duration, curr_total[1] + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Journey is over for this passenger, we can remove it since we
|
||||
# tallied the data
|
||||
del self.checkins[id]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def getAverageTime(self, startStation: str, endStation: str) -> float:
|
||||
total_duration, num_trips = self.totals[(startStation, endStation)]
|
||||
|
||||
return total_duration / num_trips
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Your UndergroundSystem object will be instantiated and called as such:
|
||||
# obj = UndergroundSystem()
|
||||
# obj.checkIn(id,stationName,t)
|
||||
# obj.checkOut(id,stationName,t)
|
||||
# param_3 = obj.getAverageTime(startStation,endStation)
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user