Compare commits
3 Commits
e793d395bd
...
58a19f7015
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 58a19f7015 | |||
| cccdd9269f | |||
| 713154644b |
34
0100_same-tree/README.md
Normal file
34
0100_same-tree/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
|||||||
|
Given the roots of two binary trees `p` and `q`, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical, and the nodes have the same value.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Example 1:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
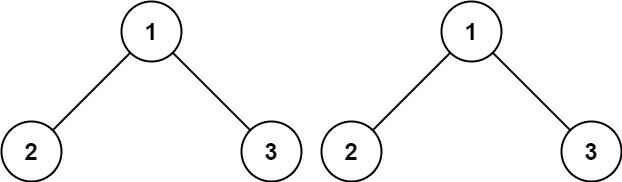
Input: p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3]
|
||||||
|
Output: true
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Example 2:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
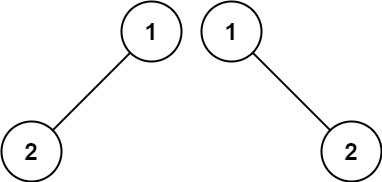
Input: p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2]
|
||||||
|
Output: false
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Example 3:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
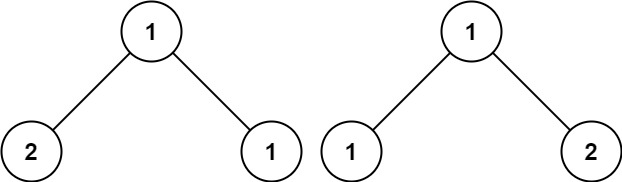
Input: p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2]
|
||||||
|
Output: false
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Constraints:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* The number of nodes in both trees is in the range `[0, 100]`.
|
||||||
|
* `-104 <= Node.val <= 104`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
https://leetcode.com/problems/same-tree/
|
||||||
14
0100_same-tree/python3/solution.py
Normal file
14
0100_same-tree/python3/solution.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
|||||||
|
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||||
|
# class TreeNode:
|
||||||
|
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||||||
|
# self.val = val
|
||||||
|
# self.left = left
|
||||||
|
# self.right = right
|
||||||
|
class Solution:
|
||||||
|
def isSameTree(self, p: Optional[TreeNode], q: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
|
||||||
|
if p is None and q is None:
|
||||||
|
return True
|
||||||
|
elif p is None or q is None or p.val != q.val:
|
||||||
|
return False
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return self.isSameTree(p.left, q.left) and self.isSameTree(p.right, q.right)
|
||||||
24
0104_maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/README.md
Normal file
24
0104_maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
|||||||
|
Given the `root` of a binary tree, return _its maximum depth_.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A binary tree's **maximum depth** is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Example 1:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
|
||||||
|
Output: 3
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Example 2:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Input: root = [1,null,2]
|
||||||
|
Output: 2
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Constraints:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[0, 104]`.
|
||||||
|
* `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree
|
||||||
0
0104_maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/python3/bfs.py
Normal file
0
0104_maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/python3/bfs.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
|||||||
|
# Time: O(N)
|
||||||
|
# Space: O(N)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||||
|
# class TreeNode:
|
||||||
|
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||||||
|
# self.val = val
|
||||||
|
# self.left = left
|
||||||
|
# self.right = right
|
||||||
|
class Solution:
|
||||||
|
maxDepthValue = 0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
|
||||||
|
'''
|
||||||
|
Recursive DFS pre-order but storing max globally
|
||||||
|
'''
|
||||||
|
def findMax(node, depth):
|
||||||
|
if node is None: return None
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
currDepth = depth + 1
|
||||||
|
self.maxDepthValue = max(currDepth, self.maxDepthValue)
|
||||||
|
findMax(node.left, currDepth)
|
||||||
|
findMax(node.right, currDepth)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
findMax(root, 0)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return self.maxDepthValue
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
|||||||
|
# Time: O(N)
|
||||||
|
# Space: O(N)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||||
|
# class TreeNode:
|
||||||
|
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||||||
|
# self.val = val
|
||||||
|
# self.left = left
|
||||||
|
# self.right = right
|
||||||
|
class Solution:
|
||||||
|
maxDepthValue = 0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
|
||||||
|
'''
|
||||||
|
Recursive DFS
|
||||||
|
'''
|
||||||
|
return 0 if root is None else 1 + max(self.maxDepth(root.left), self.maxDepth(root.right))
|
||||||
27
0543_diameter-of-binary-tree/README.md
Normal file
27
0543_diameter-of-binary-tree/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
|||||||
|
Given the `root` of a binary tree, return _the length of the **diameter** of the tree_.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The **diameter** of a binary tree is the **length** of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the `root`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The **length** of a path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Example 1:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5]
|
||||||
|
Output: 3
|
||||||
|
Explanation: 3 is the length of the path [4,2,1,3] or [5,2,1,3].
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Example 2:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Input: root = [1,2]
|
||||||
|
Output: 1
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Constraints:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[1, 104]`.
|
||||||
|
* `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
https://leetcode.com/problems/diameter-of-binary-tree/
|
||||||
36
0543_diameter-of-binary-tree/python3/solution.py
Normal file
36
0543_diameter-of-binary-tree/python3/solution.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
|||||||
|
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||||
|
# class TreeNode:
|
||||||
|
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||||||
|
# self.val = val
|
||||||
|
# self.left = left
|
||||||
|
# self.right = right
|
||||||
|
class Solution:
|
||||||
|
def diameterOfBinaryTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
|
||||||
|
result = [0]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def dfs(node):
|
||||||
|
# Leaf node height will be 1
|
||||||
|
# Empty node height will be -1
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if node is None: return -1
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lefth = dfs(node.left)
|
||||||
|
righth = dfs(node.right)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Diameter calc:
|
||||||
|
#
|
||||||
|
# Cause for current node will be pointing to both
|
||||||
|
# left and right nodes and we need to consider
|
||||||
|
# them (+2)
|
||||||
|
#
|
||||||
|
# e.g. consider this is leaf node, lefth and righth = -1
|
||||||
|
# so, current node's diameter should be 0 = 2 + -1 + -1
|
||||||
|
result[0] = max(result[0], 2 + lefth + righth)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# return max height including the node itself
|
||||||
|
return 1 + max(lefth, righth)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
dfs(root)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return result[0]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user